How do I add a filter to my view in Google Analytics?
Wednesday, December 16th, 2015
In “Admin” page, select the view you want to add a filter to and click “Filter”. On the add filter page, you will see something like this:
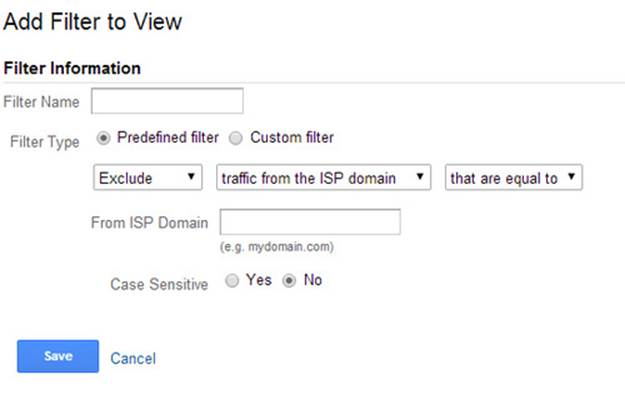
Give your filter a name such as “Sign ups” and select the filter type. For beginners, you should use predefined filters. When you learn more about regular expressions (ReGex), you can use custom filters which allows you to create more powerful implementations. To learn more about regular expressions you can go to: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/1034324?hl=en
Moving on to our “Sign ups” example, we can select “Include Only” for the first box. For the second box, we can choose “traffic to the subdirectories”. For the third box, we can choose “that are equal to”. If our website sends the user to domain.com/registration-complete/ after signing up, we can put “/registration-complete/” in the subdirectory field. You can choose whether it’s case sensitive or not and click “Save”.
Now your view “Sign ups” should track visitors who have signed up to your website only. You can experiment with other filters but make sure you do not add any filters to your “All Web Site Data” view as data that has been processed through these filters cannot be changed.
Build lasting connections through an innovative traffic exchange network that drives real visitors.

Filed under: Digital Analytics→Documentation
Tags: digital analytics, filter, Google Analytics, web analytics
Exclusive Offer!
1,500,000 Points for $110 $68. If you're running low on points — don't miss out
limited time